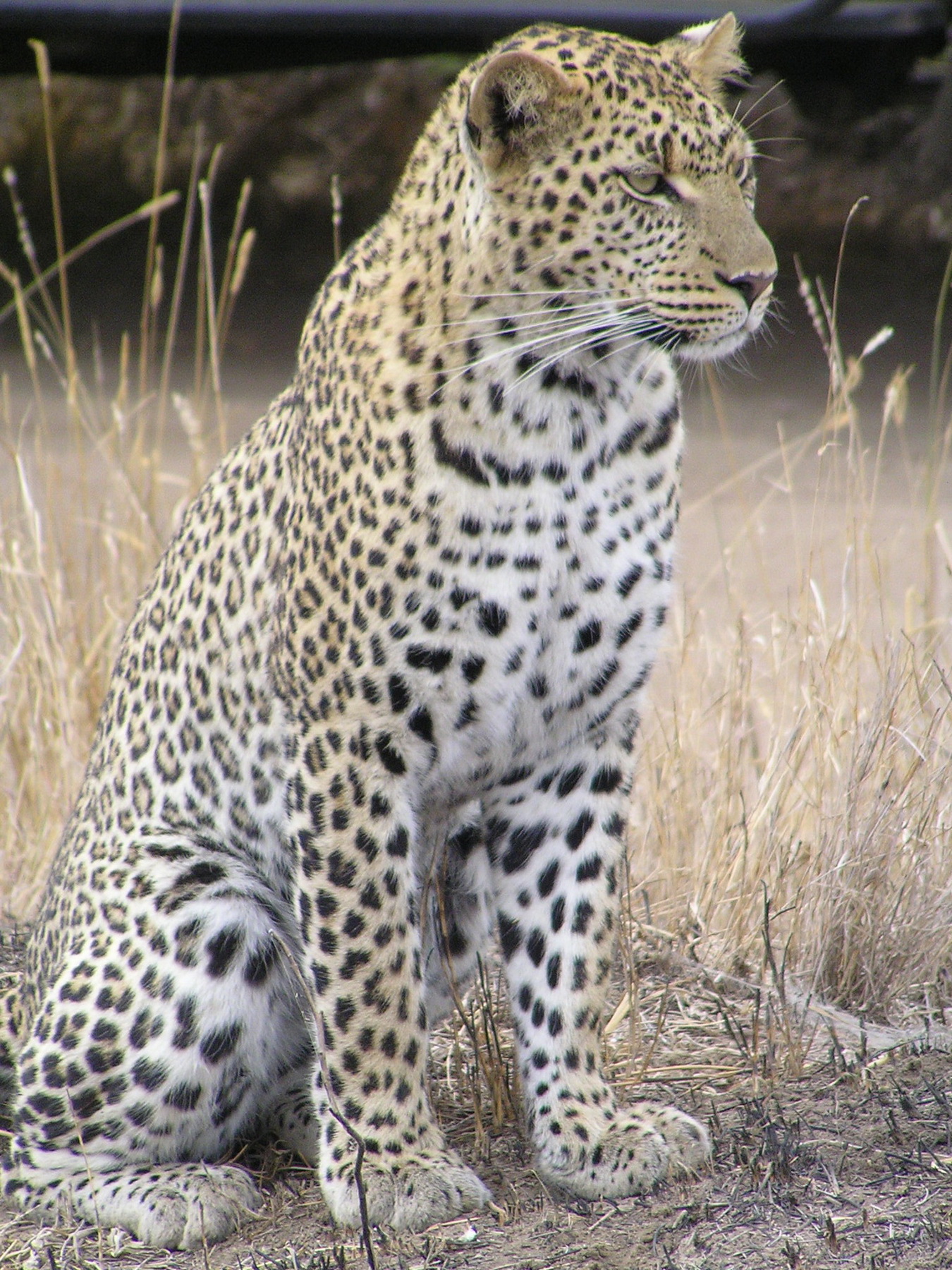
Common Leopard

Also known as Dipado, dipada, chita, tendua
Lowest risk
Native
The leopard is one of the five extant species in the genus Panthera, a member of the Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in small parts of Western and Central Asia, on the Indian subcontinent to Southeast and East Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because leopard populations are threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation, and are declining in large parts of the global range. In Hong Kong, Singapore, Kuwait, Syria, Libya, Tunisia and most likely in Morocco, leopard populations have already been extirpated. Contemporary records suggest that the leopard occurs in only 25% of its historical global range.
- Range elevation
- 5638 m (high) m
- Range mass
- 17 to 65 kg
- Range length
- 1.6 to 2.3 m
- Breeding interval
- Leopards breed every 15 to 24 months
- Breeding season
- Leopards breed year-round, with a peak during the rainy season
- Range number of offspring
- 2 to 3
- Average number of offspring
- 2
- Average gestation period
- 96 days
- Average gestation period
- 97 days
- Average weaning age
- 3 months
- Range time to independence
- 13 to 18 months
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (female)
- 2.5 years
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (female)
Sex: female - 937 days
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (male)
- 2 years
- Average age at sexual or reproductive maturity (male)
Sex: male - 771 days
- Range lifespan
Status: wild - 17 (high) years
- Range lifespan
Status: captivity - 27 (high) years
- Typical lifespan
Status: wild - 10 to 12 years
- Typical lifespan
Status: captivity - 21 to 23 years
- Range territory size
- 13 to 35 km^2
Hunt, A. 2011. "Panthera pardus" (On-line), Animal Diversity Web. Accessed November 10, 2020 at https://animaldiversity.org/accounts/Panthera_pardus/

If you notice an inaccuracy, have additional information to add, or want to suggest an edit contribute here